KMP主要应用在字符串匹配上。
KMP的主要思想是当出现字符串不匹配时,可以知道一部分之前已经匹配的文本内容,可以利用这些信息避免从头再去做匹配了。
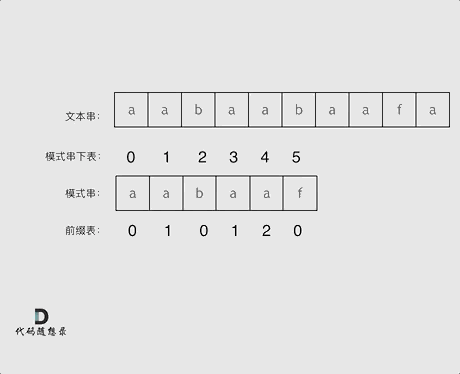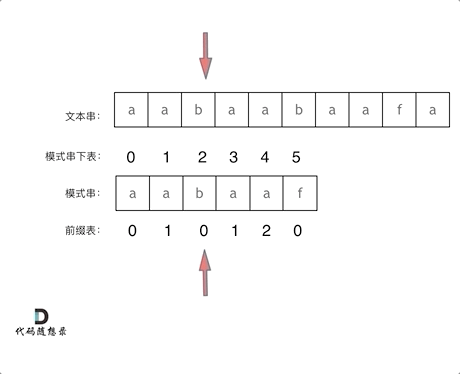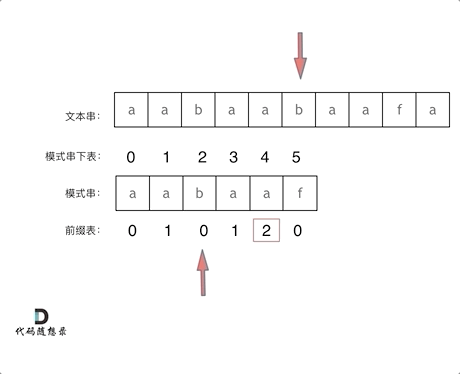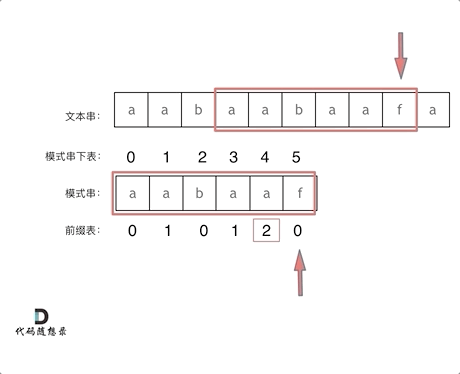
前缀表用来记录 字符串中相同的前缀与后缀字母的个数
NEXT前缀表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| void getNext(int* next, const string& s) {
int j = 0;
next[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (s[i] == s[j]) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
|
给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。
如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
使用KMP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| class Solution {
public:
void getNext(int* next, const string& s) {
int j = 0;
next[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (s[i] == s[j]) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
}
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
if (needle.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
vector<int> next(needle.size());
getNext(&next[0], needle);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.size(); i++) {
while(j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j]) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (haystack[i] == needle[j]) {
j++;
}
if (j == needle.size() ) {
return (i - needle.size() + 1);
}
}
return -1;
}
};
|



